In the previous posts [1,2] I created script for machine learning stock market price on next day prediction. But it was pointed by readers that in stock market prediction, it is more important to know the trend: will the stock go up or down. So I updated the script to predict difference between today and yesterday prices. If it is negative the stock price will go down, if positive it will go up. Below will be described implemented modifications.
Data inputting
Data from previous days are entered as features through additional columns. The number of columns can be changed through parameter N in the beginning of script. So for example for day 20 the input will contain data for day 21 as target and data for days 20, 19,18,17… 20-N
Also added differencing before scaling. Differencing helped to improve performance of network. It also makes easy to get changes from previous day. In the end the differenced data inverted back.
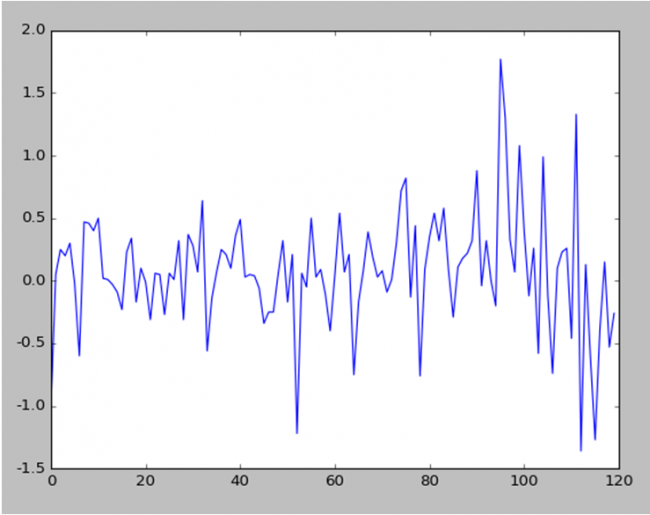
Below is the stock data prices after applying differencing (subtructing previous day stock data price from current day)
Predicting future changes
I used moving_test_window_preds function. Inside of this function the script within loop is adding new prediction to “moving window” array and removing first element from it. This is based on example from blog post on forecasting time series with LSTM[4].
So the script is predicting future day data based on the previous known data in the “moving window”, updating known data and starting again. The performance evaluated by comparing predicted data with test (not used before) data.
LSTM Configuration
The LSTM network is constructed as following:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | model = Sequential ()input_shape =(len(cols), 1) ))model.add (LSTM ( 400, activation = 'relu', inner_activation = 'hard_sigmoid' , bias_regularizer=L1L2(l1=0.01, l2=0.01), input_shape =(len(cols), 1), return_sequences = False ))model.add(Dropout(0.3))from keras import optimizersmodel.add (Dense (output_dim =1, activation = 'linear', activity_regularizer=regularizers.l1(0.01)))adam=optimizers.Adam(lr=0.01, beta_1=0.89, beta_2=0.999, epsilon=None, decay=0.0, amsgrad=True)model.compile (loss ="mean_squared_error" , optimizer = "adam") history=model.fit (x_train, y_train, batch_size =1, nb_epoch =1400, shuffle = False, validation_split=0.15) |
Weight regularization together with differencing helped to decrease overfitting.
Results
Performance of NN is 88% : 8 correct data out of 9. Below are the data charts that comparing predicted data (9 first days from 22 total days) with actual test data. Below you can find output chart and full python source code.
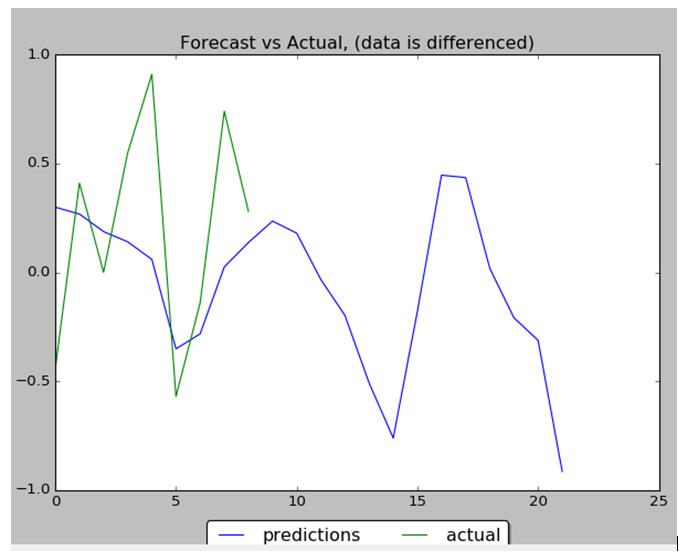
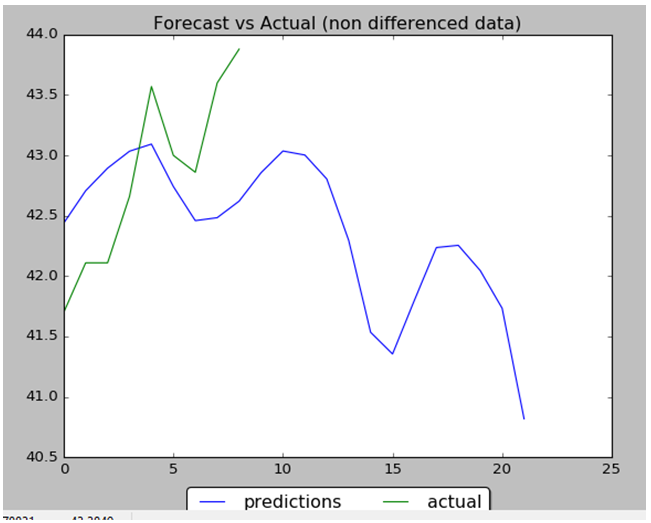
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 | import numpy as npimport pandas as pdfrom sklearn import preprocessingimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib.ticker as mtickfrom keras.regularizers import L1L2fname="C:\\Users\\Leo\\Desktop\\A\\WS\\stock data analysis 2017\\GM.csv"data_csv = pd.read_csv (fname)#how many data we will use # (should not be more than dataset length )data_to_use= 150# number of training data# should be less than data_to_usetrain_end =120total_data=len(data_csv)#most recent data is in the end #so need offsetstart=total_data - data_to_useyt = data_csv.iloc [start:total_data ,4] #Close priceyt_ = yt.shift (-1) print (yt_)data = pd.concat ([yt, yt_], axis =1)data. columns = ['yt', 'yt_']N=18 cols =['yt']for i in range (N): data['yt'+str(i)] = list(yt.shift(i+1)) cols.append ('yt'+str(i)) data = data.dropna()data_original = datadata=data.diff()data = data.dropna() # target variable - closed price# after shiftingy = data ['yt_']x = data [cols] scaler_x = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler ( feature_range =( -1, 1))x = np. array (x).reshape ((len( x) ,len(cols)))x = scaler_x.fit_transform (x)scaler_y = preprocessing. MinMaxScaler ( feature_range =( -1, 1))y = np.array (y).reshape ((len( y), 1))y = scaler_y.fit_transform (y) x_train = x [0: train_end,]x_test = x[ train_end +1:len(x),] y_train = y [0: train_end] y_test = y[ train_end +1:len(y)] x_train = x_train.reshape (x_train. shape + (1,)) x_test = x_test.reshape (x_test. shape + (1,))from keras.models import Sequentialfrom keras.layers.core import Densefrom keras.layers.recurrent import LSTMfrom keras.layers import Dropoutfrom keras import optimizersfrom numpy.random import seedseed(1)from tensorflow import set_random_seedset_random_seed(2)from keras import regularizersmodel = Sequential ()model.add (LSTM ( 400, activation = 'relu', inner_activation = 'hard_sigmoid' , bias_regularizer=L1L2(l1=0.01, l2=0.01), input_shape =(len(cols), 1), return_sequences = False ))model.add(Dropout(0.3))model.add (Dense (output_dim =1, activation = 'linear', activity_regularizer=regularizers.l1(0.01)))adam=optimizers.Adam(lr=0.01, beta_1=0.89, beta_2=0.999, epsilon=None, decay=0.0, amsgrad=True)model.compile (loss ="mean_squared_error" , optimizer = "adam") history=model.fit (x_train, y_train, batch_size =1, nb_epoch =1400, shuffle = False, validation_split=0.15)y_train_back=scaler_y.inverse_transform (np. array (y_train). reshape ((len( y_train), 1)))plt.figure(1)plt.plot (y_train_back)fmt = '%.1f'tick = mtick.FormatStrFormatter(fmt)ax = plt.axes()ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(tick)print (model.summary())print(history.history.keys())plt.figure(2)plt.plot(history.history['loss'])plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'])plt.title('model loss')plt.ylabel('loss')plt.xlabel('epoch')plt.legend(['train', 'test'], loc='upper left')fmt = '%.1f'tick = mtick.FormatStrFormatter(fmt)ax = plt.axes()ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(tick)score_train = model.evaluate (x_train, y_train, batch_size =1)score_test = model.evaluate (x_test, y_test, batch_size =1)print (" in train MSE = ", round( score_train ,4)) print (" in test MSE = ", score_test )pred1 = model.predict (x_test) pred1 = scaler_y.inverse_transform (np. array (pred1). reshape ((len( pred1), 1))) prediction_data = pred1[-1] model.summary()print ("Inputs: {}".format(model.input_shape))print ("Outputs: {}".format(model.output_shape))print ("Actual input: {}".format(x_test.shape))print ("Actual output: {}".format(y_test.shape))print ("prediction data:")print (prediction_data)y_test = scaler_y.inverse_transform (np. array (y_test). reshape ((len( y_test), 1)))print ("y_test:")print (y_test)act_data = np.array([row[0] for row in y_test])fmt = '%.1f'tick = mtick.FormatStrFormatter(fmt)ax = plt.axes()ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(tick)plt.figure(3)plt.plot( y_test, label="actual")plt.plot(pred1, label="predictions")print ("act_data:")print (act_data)print ("pred1:")print (pred1)plt.legend(loc='upper center', bbox_to_anchor=(0.5, -0.05), fancybox=True, shadow=True, ncol=2)fmt = '$%.1f'tick = mtick.FormatStrFormatter(fmt)ax = plt.axes()ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(tick)def moving_test_window_preds(n_future_preds): ''' n_future_preds - Represents the number of future predictions we want to make This coincides with the number of windows that we will move forward on the test data ''' preds_moving = [] # Store the prediction made on each test window moving_test_window = [x_test[0,:].tolist()] # First test window moving_test_window = np.array(moving_test_window) for i in range(n_future_preds): preds_one_step = model.predict(moving_test_window) preds_moving.append(preds_one_step[0,0]) preds_one_step = preds_one_step.reshape(1,1,1) moving_test_window = np.concatenate((moving_test_window[:,1:,:], preds_one_step), axis=1) # new moving test window, where the first element from the window has been removed and the prediction has been appended to the end print ("pred moving before scaling:") print (preds_moving) preds_moving = scaler_y.inverse_transform((np.array(preds_moving)).reshape(-1, 1)) print ("pred moving after scaling:") print (preds_moving) return preds_moving print ("do moving test predictions for next 22 days:") preds_moving = moving_test_window_preds(22)count_correct=0error =0for i in range (len(y_test)): error=error + ((y_test[i]-preds_moving[i])**2) / y_test[i] if y_test[i] >=0 and preds_moving[i] >=0 : count_correct=count_correct+1 if y_test[i] < 0 and preds_moving[i] < 0 : count_correct=count_correct+1accuracy_in_change = count_correct / (len(y_test) )plt.figure(4)plt.title("Forecast vs Actual, (data is differenced)") plt.plot(preds_moving, label="predictions")plt.plot(y_test, label="actual")plt.legend(loc='upper center', bbox_to_anchor=(0.5, -0.05), fancybox=True, shadow=True, ncol=2)print ("accuracy_in_change:")print (accuracy_in_change)ind=data_original.index.values[0] + data_original.shape[0] -len(y_test)-1prev_starting_price = data_original.loc[ind,"yt_"]preds_moving_before_diff = [0 for x in range(len(preds_moving))]for i in range (len(preds_moving)): if (i==0): preds_moving_before_diff[i]=prev_starting_price + preds_moving[i] else: preds_moving_before_diff[i]=preds_moving_before_diff[i-1]+preds_moving[i]y_test_before_diff = [0 for x in range(len(y_test))]for i in range (len(y_test)): if (i==0): y_test_before_diff[i]=prev_starting_price + y_test[i] else: y_test_before_diff[i]=y_test_before_diff[i-1]+y_test[i]plt.figure(5)plt.title("Forecast vs Actual (non differenced data)")plt.plot(preds_moving_before_diff, label="predictions")plt.plot(y_test_before_diff, label="actual")plt.legend(loc='upper center', bbox_to_anchor=(0.5, -0.05), fancybox=True, shadow=True, ncol=2)plt.show() |
References
1. Time Series Prediction with LSTM and Keras for Multiple Steps Ahead
2. Machine Learning Stock Prediction with LSTM and Keras
3. Data File
4. Using LSTMs to forecast time-series








You must be logged in to post a comment.